1. Overview
Softmax is a common layer in neural network, but when the nubmer of output class increases, the performance of softmax layer get decreased. For example, in Language Model(LM) task, the vocabulary is usually very larget, for example in 1 Billion Word Language Model Benchmark, the vocabulary is about 80K, while in languages such as chinese and japanese, the vocabulary can be up to 100K[1]. Such large vocabulary brings challenges to softmax, both in training and inferencing phase. So, some methods are proposed to accelerating softmax.
2. Sampling Based Methods
2.1 Sampled Softmax
When calculating softmax over a large vocabulary, we must iterate over all the whole vocabulary to calculate the partition function. Sampled Softmax[2] calculate on a small subset of vocabulary instead of the whole vocabulary, the subset is sampled from a distribution $Q$
2.2 Noise Contrasive Estimation
NCE[3] transform the softmax multi-label classification problem into 2-label classification problem. NCE introduces a noise distribution $Q$, and samples negative samples from this distribution, the loss function os NCE is
where
and
2.3 Negative sampling
NEG can be viewed as a special kink of NCE where $kQ(w) = 1$
3. Softmax Based Methods
3.1 Hierachical softmax
Hierachical softmax organizes vocabulary into a tree, where leaf nodes are words in the vocabulary, and internal nodes are latent variables. The probability of a certain word in the vocabulary is the product of the probabilities of all the nodes in the path from the root node to the corresponding word leaf node. If the built tree is perfectly balanced, the training compelxity can be reduce to $ O(logV) $.
A popular strategy to cluster words is based on frequency. Words are sorted by frequency, and then slices sorted words into clusters that contain an equal share of total probability. Strategies such as k-means can also be used.
3.2 Differentiated Softmax
Differentiated softmax[4] is based on the intuition that words in the vocabulary are not equal, frequent words need more information to predict them, while infrequent ones need less.
So, instead of using a dense $d_{hidden} * |V|$ matrix, D-softmax uses many small matrices.
As shown in following picture
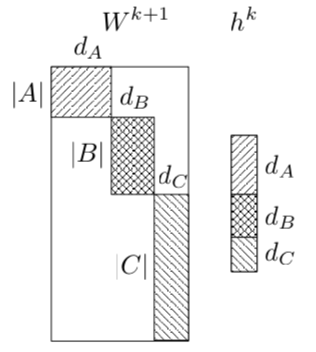
the dense matrix $d_{hidden}*|A|$ is replaced by the three small matrices $d_A * |A|$, $d_B * |B|$ and $d_C * |C|$. In this way, big matrix multiplication is avoided by doing three small matrix multiplications, so in train and reference phases, computation complixity is reduced.
3.3 Differentiated Softmax[*]
D-Softmax[*] is similar to D-Softmax, but differs in that it doesn’t split the hidden state to samll splits, instead, it uses projection matrices of different size to map the whole hidden state to different words cluster
3.4 Adaptive Softmax
Adaptive Softmax is a kind of HSM, but is optimized to construct the tree structure (cluster numbers, cluster data, etc.) so that the overall GPU computation time is minimized.
Besides, Adaptive Softmax doesn’t put all of words in the leaf node, some words are put in the internal nodes, as shown below
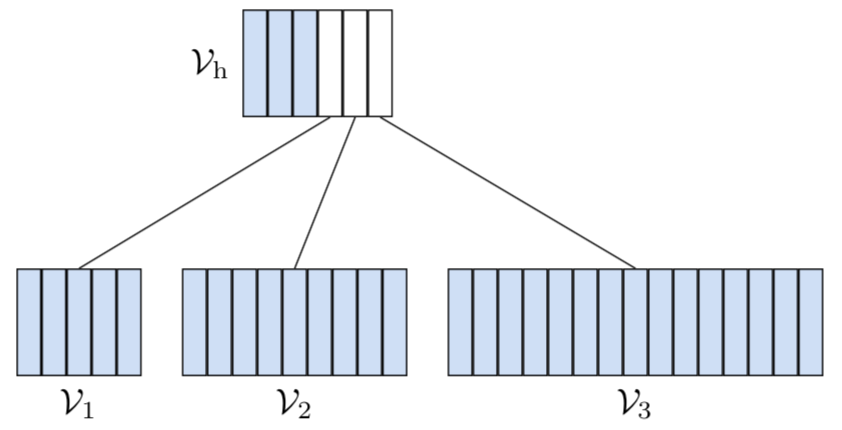
References
[1] JLM - Fast RNN Language Model with Large Vocabulary
[2] On Using Very Large Target Vocabulary for Neural Machine Translation
[3] Notes on Noise Contrastive Estimation and Negative Sampling
[4] Strategies for Training Large Vocabulary Neural Language Models
[5] Efficient softmax approximation for GPUs
[6] http://ruder.io/word-embeddings-softmax/index.html#noisecontrastiveestimation