1. Overview
As the development of deep learning, neural machine translation gradually replaces stochastic machine translation. Usually NMT model contain massive parameters, thus requires a big parallel corpus for supervised learning. However, parallel corpus is very ‘expensive’, especially for some minority languages, thus some semisupervised or even unsupervised models are proposed.
2. Supervised NMT
2.1 A Encoder-Decoder model
[1] applies encoder-decocer model to machine translation, in this model, a LSTM encoder encodes the entire source sentence to a fix-length vector, and then a LSTM decoder generates the target sentece in an auto-regressive way
an special ‘<EOS>’ token is used to trigger the begin of generation and also indicate the end of generation
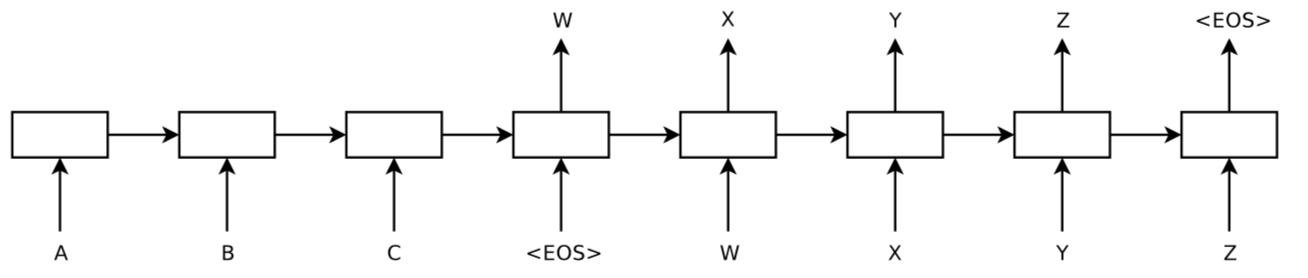
A trick of reversing the source sentence is applied to improve the performance, the reason is that although LSTM is capable of solving long dependency, by reversing the source sentence, some shorter dependencies will be introduced, and better ‘communication’ will be established between these items of short dependency, and finally induces an overall performance improvements
2.2 Attention mechanism
In encoder-decoder model, source sentence is encoded to a fixed length vector, an then decoder generate target sentence based on this fixed length vector. The use of a fixed length vector is a bottleneck in performance, [2] use attention mechanism to solve this problem. Attention mechisim works by allowing decoder to soft-search encoder outputs when predicting a target word
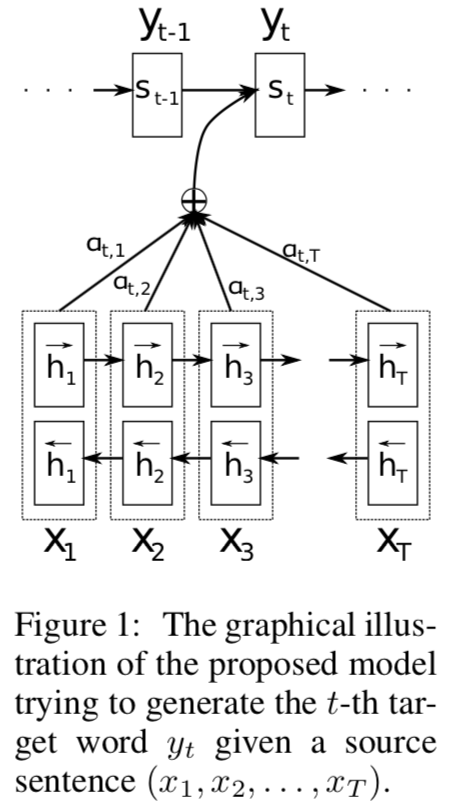
the corresponding formula is
where
2.3 ConvS2S
In encoder-decoder model, RNN structures are usually used to model sequence inputs in encoder module and sequence generation in decoder module. However, the procedure of RNN is sequential, which slow down the train/inference speed of model. So, many papers such as [3] and [4] try to use other network structure to replace RNN. ConvS2S model[3] uses CNN, compared to RNN, stacked CNN can efficiently capture long dependency and local feature the structure of ConvS2S is as following
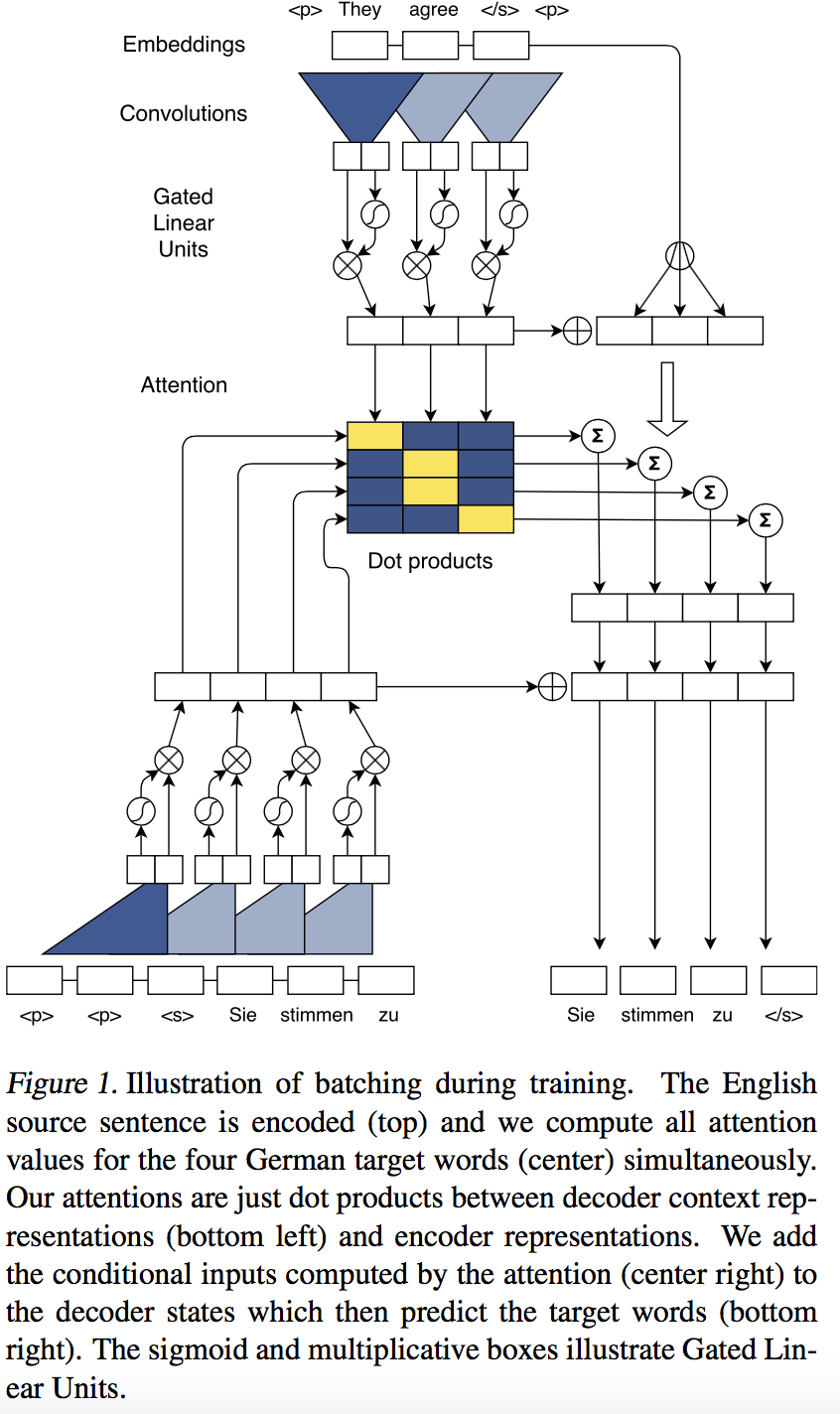
In that CNN doesn’t model the sequential information, a special postion embedding is used to inform the model of sequential information
It is remarkable that the encoding process is still auto-regressive, to keep the consistency between training and inferencing, when training, a mask is applied to prevent the model from infering to future information. [4] also uses this trick
2.4 Transformer
[4] uses only attention mechanism
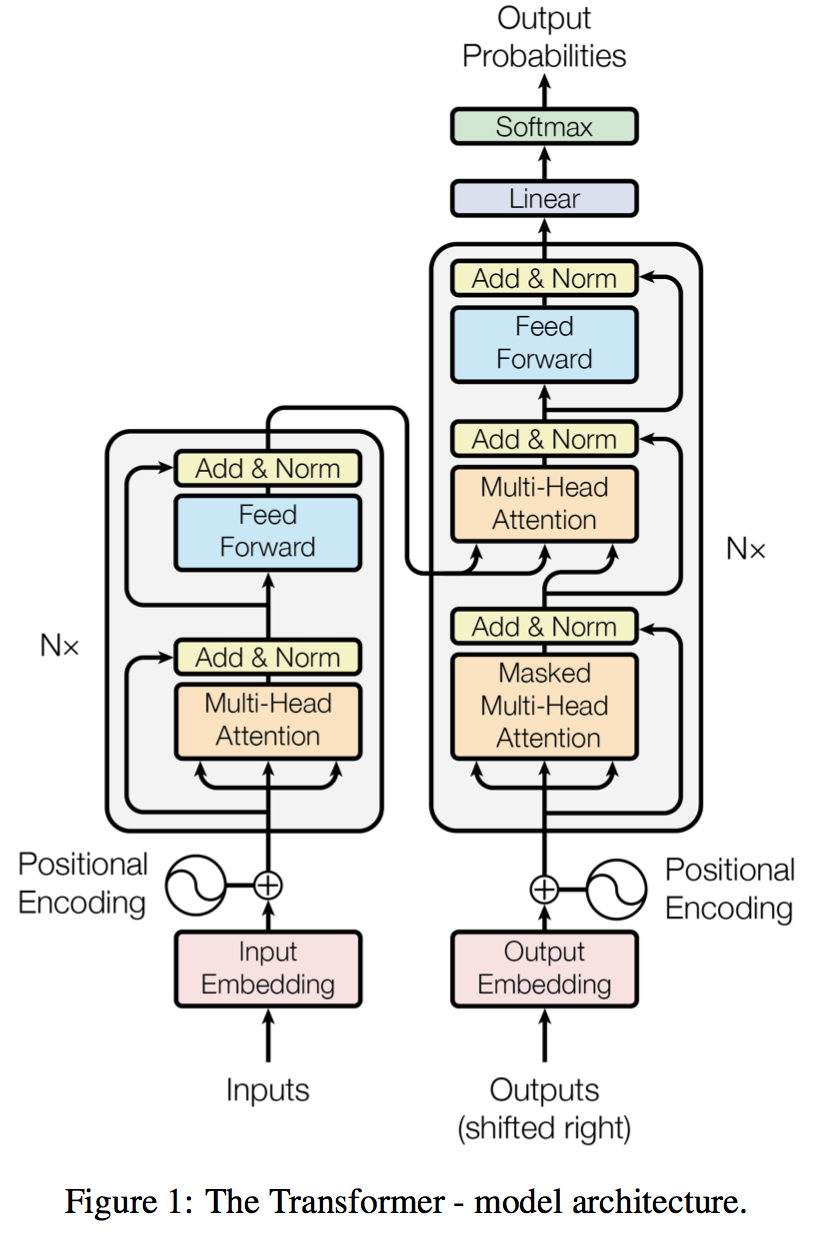
self-attention and multi-head attention is used in the model to form the basic model block, and the encoder module and decoder module of transformer is constructed by stacking the same block units
Self-attention, sometimes called intra-attention is an attention mechanism relating different positions of a single sequence in order to compute a representation of the sequence
Transformer uses a particular attention ‘Scaled Dot-Product Attention’
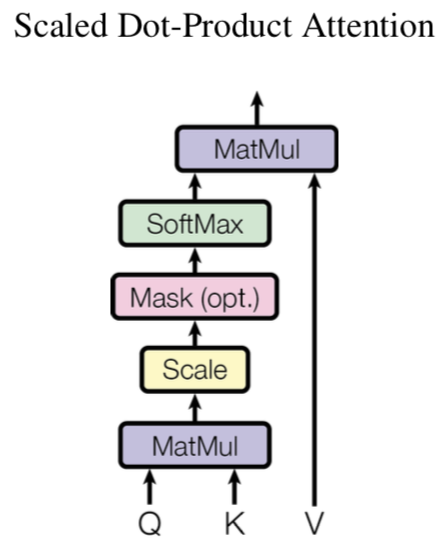
Mult-head attention uses different mapping matrix to map inputs to different spaces, and then calculates attention in these spaces, and finally, concat all the results and mapping back to the original spaces
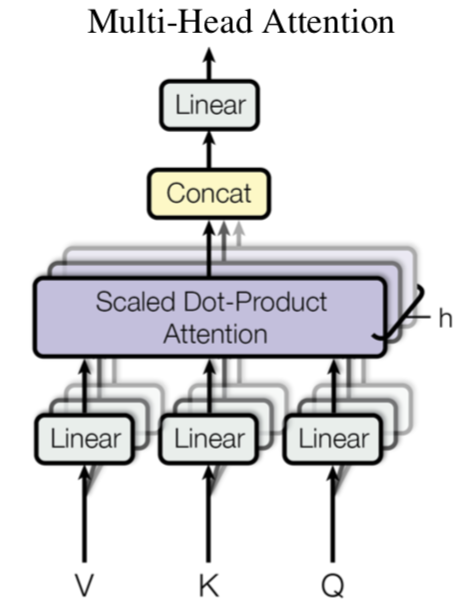
where
[4] also applies a position encoding method to add position features
3. Semi-supervised/unsupervised NMT
3.1 Dual learning
[5] regards NMT process as a dual process, for example, the En-Fr translation task can be regarded as a dual task of Fr-En translation task. And in the dual learning setting, monolingual data is utilized to assist parallel data.
Two methods are proposed to deal with monolingual data
-
Training language model to evaluate the generate translation
-
Generating pesudo parallel data from on translator for the other one
the detailed algorithm is as following

3.2 Unsupervised learning
[6] proposes the following unsupervised learning framework LANG1-LANG2 translator and the dual LANG2-LANG1 translator are both of encoder-decoder structure
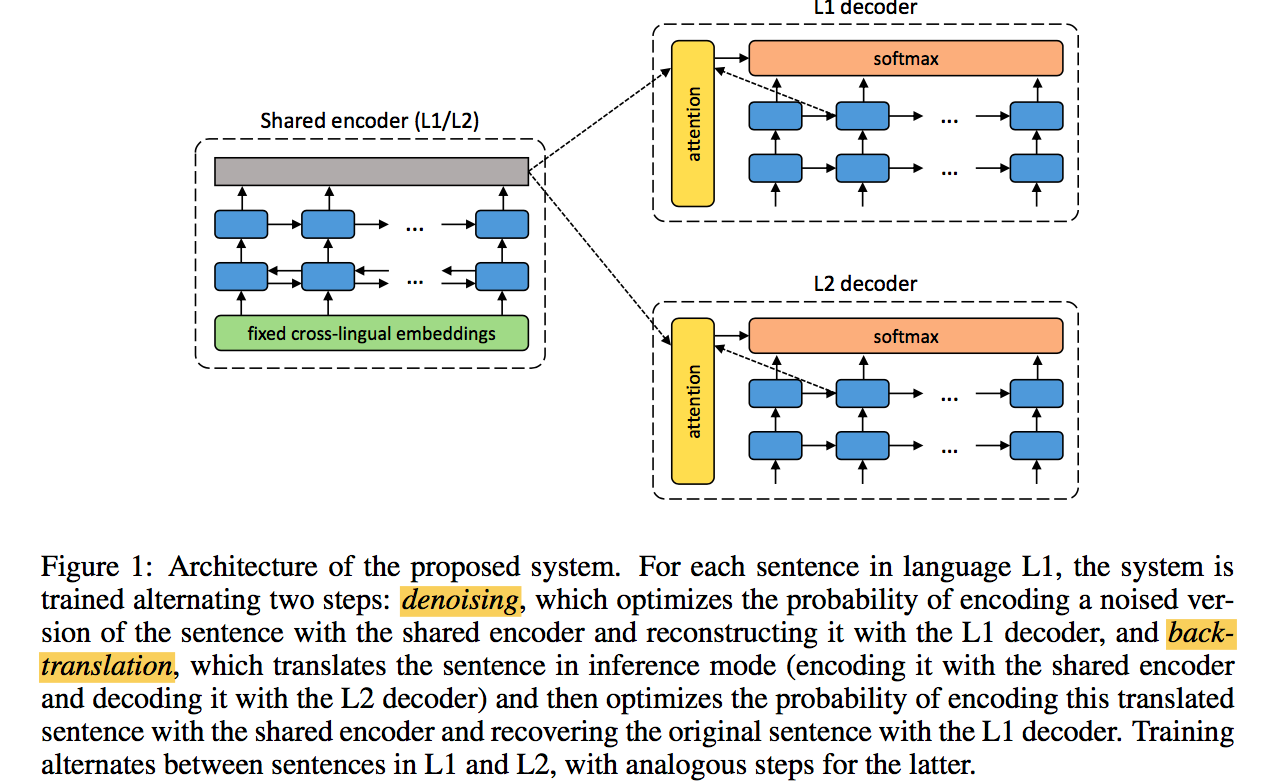
the tow translators share a common encoder, but have their exclusive decoder
and the training process is the interleaving of the following subprocess
-
Denoise AutoEncoder LANG1 is encoded by the share encoder(with multilingual embedding[7]), and is recovered to itself by the LANG2-LANG1 translator decoder. The noise is added so that the model won’t be trained to a simply copy-paste model
-
Backtranslation Use one translotor, for exmpale, LANG1-LANG2 translator to produce pesudo parallel data, and use the generated data to train LANG2-LANG1 translator
The process of NMT as two-step framework: mapping a source sentence to a vector in hidden space, and then mapping the vector to target sentence. [7] assumes that the the source and target languages share a same hidden space, and the NMT training process can be optimized by minimizing reconstruction loss. And there are mainly two reconstruction processes
-
reconstruct the sentence from the noised hidden space vector corresponding to the sentence itself(Similar to DAE)
-
Similar to backtranslation, reconstruct LANG1 sentence from the noised LANG2 sentence (generated by translate from LANG1 sentence itself)
Additionaly, an adversarial loss is proposed to resitrict LANG1 and LANG2 to share a same hidden space.
4. Pivot-based NMT
In pivot-based NMT setting, source-pivot translator and pivot-target translator are available, and source-target translator is the translator to be trained.
A naive method is to use source-pivot and pivot-target translator to produce pesudo parallel data, however in this method, we need sample to get pivot sentence, and then sample to get target sentence, in the sample process, information are lost. [9] proposes to use Expected Word Embeddings to alleviate this problem.
References
[1] Sequence to Sequence Learning with Neural Networks
[2] NEURAL MACHINE TRANSLATION BY JOINTLY LEARNING TO ALIGN AND TRANSLATE
[3] Convolutional Sequence to Sequence Learning
[4] Attention is all you need
[5] Dual Learning for Machine Translation
[6] UNSUPERVISED NEURAL MACHINE TRANSLATION
[7] Learning bilingual word embeddings with (almost) no bilingual data
[8] Unsupervised Machine Translation Using Monolingual Corpora Only
[9] Maximum Expected Likelihood Estimation for Zero-Resource Neural Machine Translation